Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson, students should be able to:
i. Explain the nutritional importance of carbohydrates as a primary energy source.
ii. Describe the different types of carbohydrates and their varying energy-providing capacities.
iii. Identify the role of glucose as the body's preferred fuel and its metabolic fate.
iv. Understand the concept of energy storage in the form of glycogen and its significance for physical activities.
v. Appreciate the importance of balancing carbohydrate intake to meet energy demands and maintain overall health.
Introduction
Carbohydrates, a fundamental component of a balanced diet, play a pivotal role in providing energy for the body's various functions. They serve as the primary energy source, fueling cellular processes that support muscle contraction, brain activity, and overall metabolism. Understanding the nutritional significance of carbohydrates and their role as energy storage molecules is essential for appreciating their dietary importance.
i. Nutritional Importance of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are essential macronutrients, providing approximately 40-60% of the body's total energy needs. They are readily broken down into glucose, the body's preferred fuel, which enters metabolic pathways to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
ii. Types of Carbohydrates and Energy-Providing Capacities
Carbohydrates are classified into two main categories: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates, such as table sugar and white bread, are quickly digested and release glucose rapidly into the bloodstream. Complex carbohydrates, like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are digested more slowly, providing a sustained release of glucose over time.
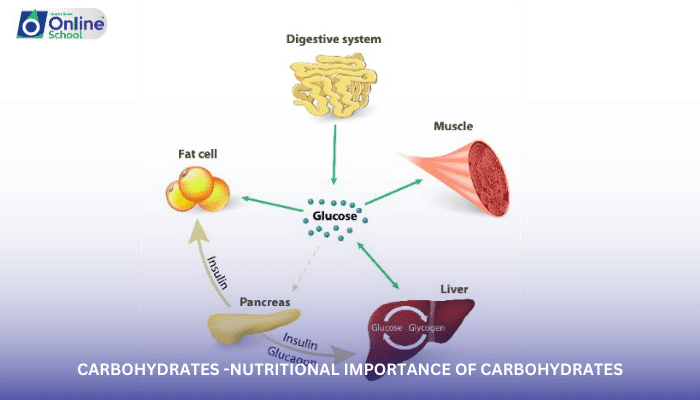
iii. Glucose as the Body's Preferred Fuel
Glucose, the primary end product of carbohydrate digestion, is the body's preferred fuel for energy production. It is transported to cells through the bloodstream, where it enters metabolic pathways in the mitochondria to generate ATP. ATP, the energy currency of cells, powers various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and protein synthesis.
iv. Energy Storage in the Form of Glycogen
The body stores excess glucose in the form of glycogen, a complex carbohydrate, primarily in the liver and muscles. Glycogen serves as a readily available energy reserve, providing glucose during periods of physical activity or when dietary carbohydrate intake is low.
v. Balancing Carbohydrate Intake for Energy Needs and Health
While carbohydrates are essential for energy needs, excessive consumption can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of developing chronic diseases. Balancing carbohydrate intake is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being.Carbohydrates play a fundamental role in human nutrition, providing energy for various bodily functions. Understanding the different types of carbohydrates, their energy-providing capacities, and the role of glucose as the body's preferred fuel is essential for making informed dietary choices that support overall health and well-being.